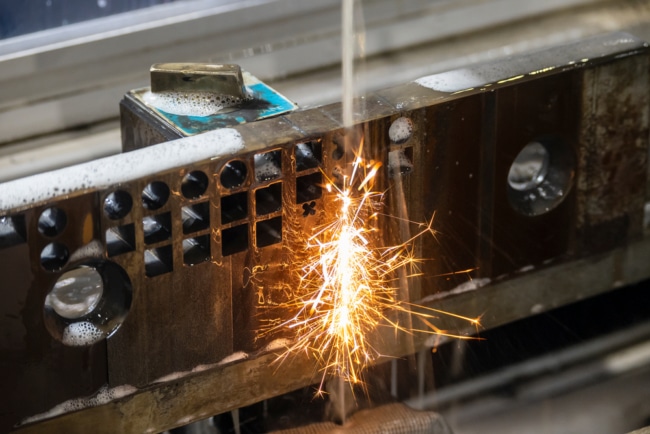
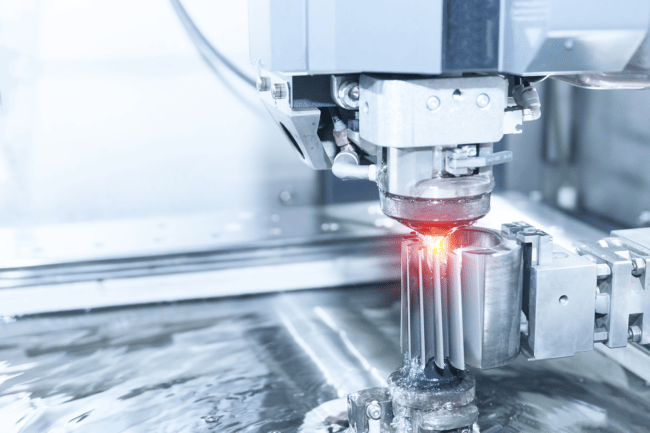
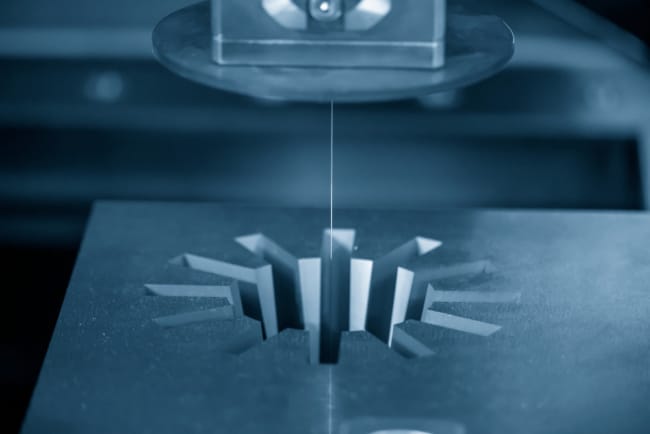
You might wonder, “what is the CNC turning process” if you have been around manufacturing for a while. Simply defined, CNC turning is spinning materials at high speed and applying a cutting tool to remove materials. This can be applied to various materials, and the resulting product is determined by the angle of the cutting tool. CNC is important in manufacturing because it is highly accurate, cuts production times and is relatively safer than other types of cutting.
What is the CNC Turning Process?
CNC, or Computer Numerical Control, takes advantage of automation to subtractively cut materials. As cutting tools spin, materials move along the horizontal axis of the part. However, you can use multi-axis CNC mills for more complex tasks. CNC machines operate via a cartesian coordinate system, which is input via software. From there, the machine automatically moves to the set coordinates in a set pattern to subtractively sculpt parts for your projects.
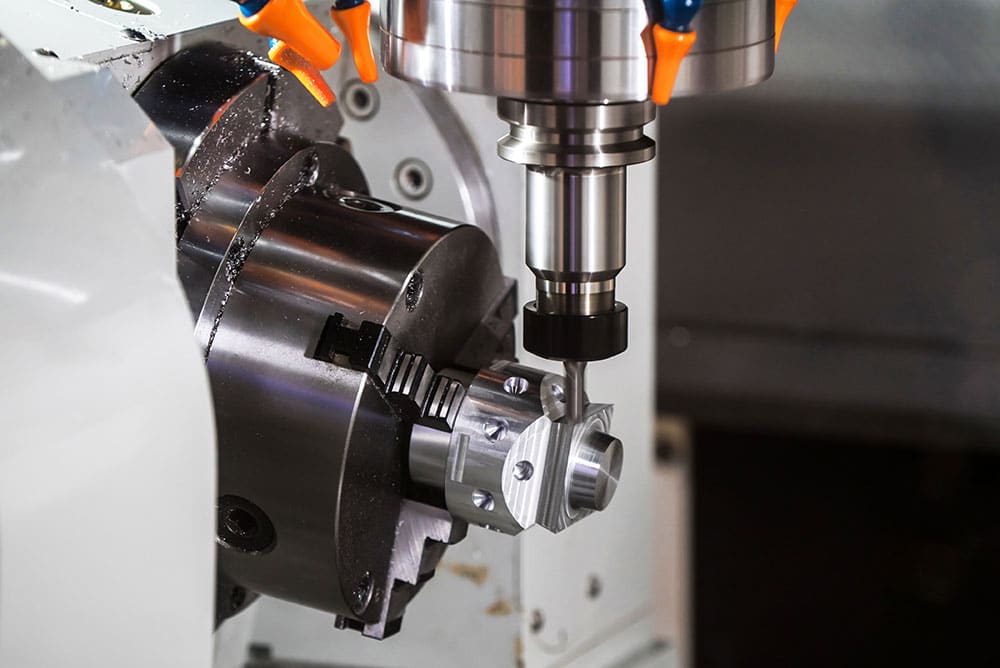
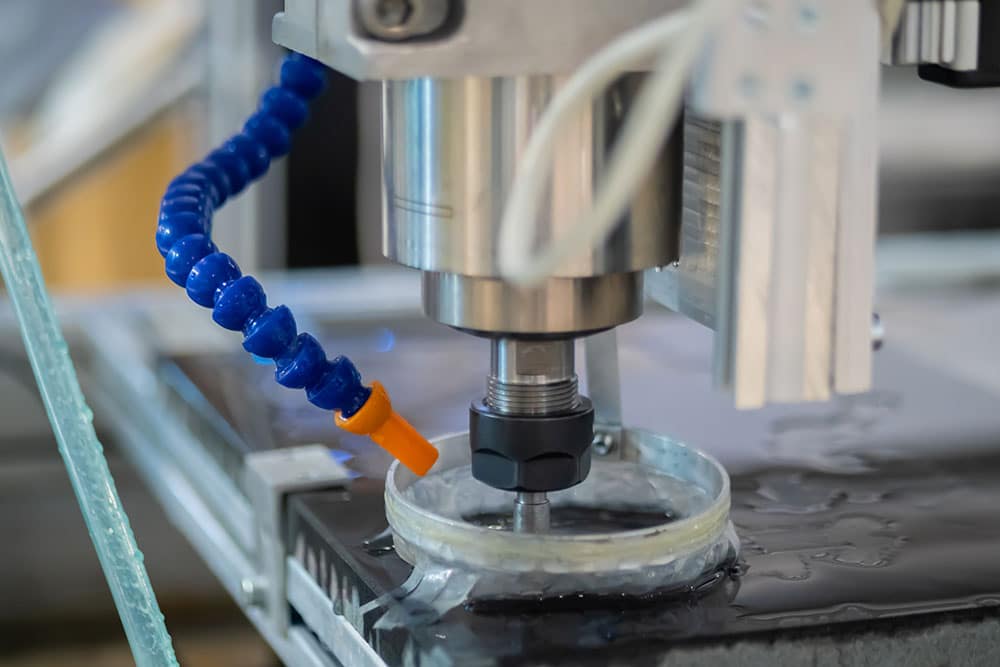
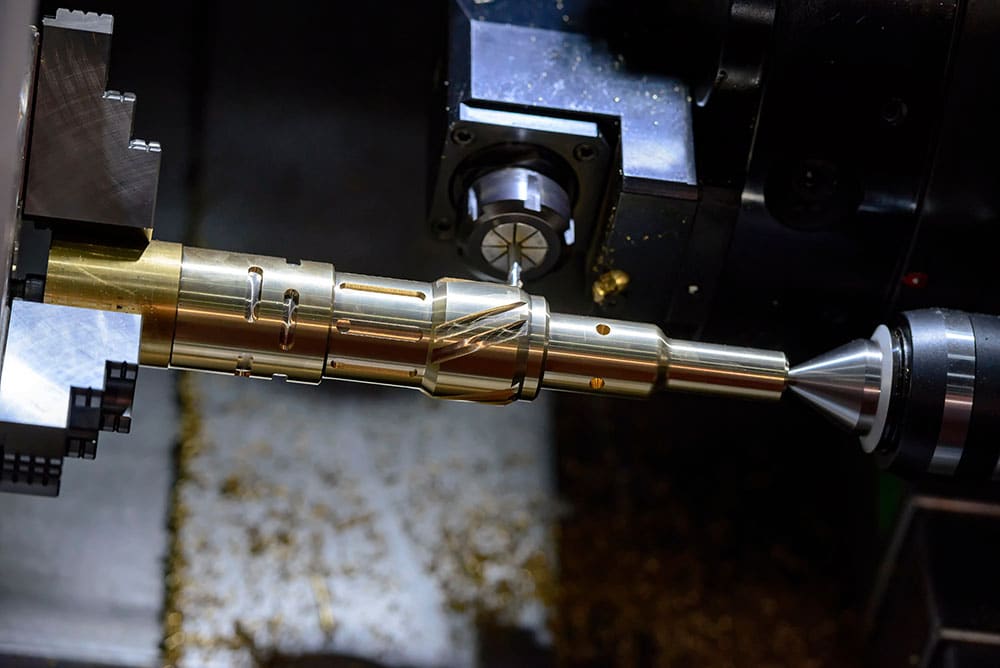



CNC Turning Operations Explained
CNC turning requires multiple components such as a mill, lathe and raw material. There are four main steps in a CNC turning project[1] that must be followed in order. Modern CNC machines are much easier to use than older ones and can link directly to CAD and CAM apps:
Key Steps
- The first step is to create a digital model in CAD and CAM software of your product.
- Next, you export your CAD file to create machining code such as M-code and G-code[2].
- You must also set up your lathe that will follow the coordinates in your code file.
- Finally, the machine can manufacture parts by turning in relation to the code file.
Of course, these are the basic steps required for machining. And each step has sub-processes involved in the configuration. For example, you must turn off the machine, load a CNC lathe and calibrate the lathe when setting up the lathe before you execute the program and cutting.
CNC Machine Materials
A CNC machine is very complex and is made up of various components. Apart from the specialised industrial computer, there is also other manufacturing equipment within the machining area. For cutting alone, there are several different tools, such as drill bits, mills and gear cutters[3]. Because of this, CNC machines are amazingly versatile and able to do pretty much anything related to cutting. Of course, with supreme speed, efficiency and accuracy.
As useful as a CNC machine is, and how almost unlimited the uses are, there are only a handful of materials you can use for a CNC project. However, the materials are some of the most commonly found in manufacturing, and some aren’t so common. For instance, you can CNC standard manufacturing materials such as steel, aluminium, and brass. But you can also use exotic and modern industrial materials such as carbon steel and even synthetics like nylon.
The Benefits of CNC Turning
The primary benefits of CNC turning are numerous. At a glance, CNC offers a high degree of accuracy, flexibility for multi-use applications, exact replication, very quick results, and above all, a high degree of safety. These are all common advantages you would look for concerning a modern manufacturing project. Using CAD and CAM systems allows you to produce highly accurate prototypes that do not deviate from original designs, meaning each cut is perfect.
Accurate repetition is a huge advantage of CNC machining. And being able to switch production at the touch of a button allows you to complete multiple custom projects at the same time. But the primary benefit of CNC is the safety aspect. The CNC system itself is safe. But it’s how you use it that causes problems with material ejections, dust and sharp objects. Modern CNC machines use coolant systems that ventilate the area. Yet improper use will cause injury.
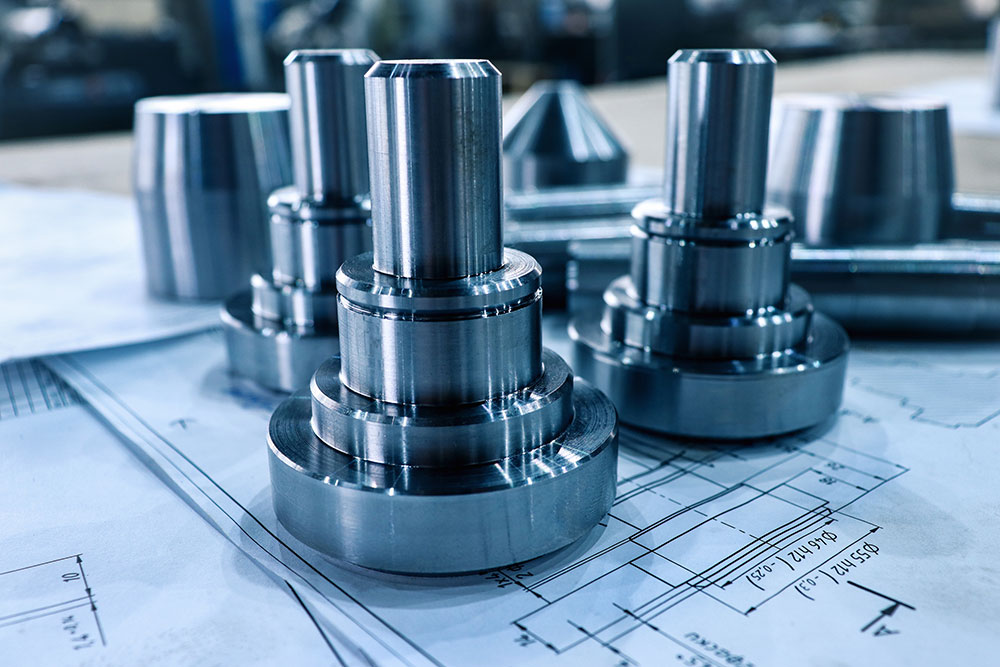

Applications of Laser Welding
CNC has changed how parts are made. Precision engineering is now possible with minimal error due to human input. As such, the applications for CNC in manufacturing complex parts reach far and wide. Industries that use CNC the most include the medical field for custom parts, the aerospace industry, which requires strength and precision, and of course, the manufacture of electronic components. So, anything that isn’t hand-made uses CNC tools.
The uses for CNC and the applications thereof mean CNC engineering is among the most widely used methods in manufacturing today. And the precision of the technology is getting better all the time.
From tiny parts to large-scale projects, here are some great examples:
- Jewellery and accessories are among the most common CNC router projects.
- Basic yet precise products like wall tiles, chopping boards and even ash trays.
- Precise electronic components such as printed circuit boards for smartphones.
- Repeated manufacture of parts that wear down and need periodic replacement.
- You can even use your CNC to make spare CNC machine parts to sell or use.
The list is almost endless when it comes to making things with a CNC machine. If you can think of it, a CNC machine might be able to make it. CNC is used widely in mass production. But like 3D printing, it comes into its own for making custom parts for personal projects or special items.
CNC technology has come a long way since its infancy. And like all modern technologies, the applications and developments in CNC manufacturing are getting better. A higher speed and improved accuracy are to be expected. However, smart monitoring is becoming more prevalent. For example, adaptive processes can adjust manufacture based on tool wear, breakage and stability, making adjustments in real time. And AI can accurately predict operational periods.
Conclusion
CNC is a vital tool in any manufacturing process. The high degree of accuracy, speed and repeated manufacture make it invaluable for large-scale projects and projects that require specialist designs. Yet CNC machining is also among the safest ways to manufacture when used correctly. Like all technological innovations, CNC turning is currently improving with modern tech such as smart controls and AI for real-time monitoring and control adjustments.
Related Content
Need more information?
To see how A&M could support your next complex manufacturing project – simply call us, or use the form below.