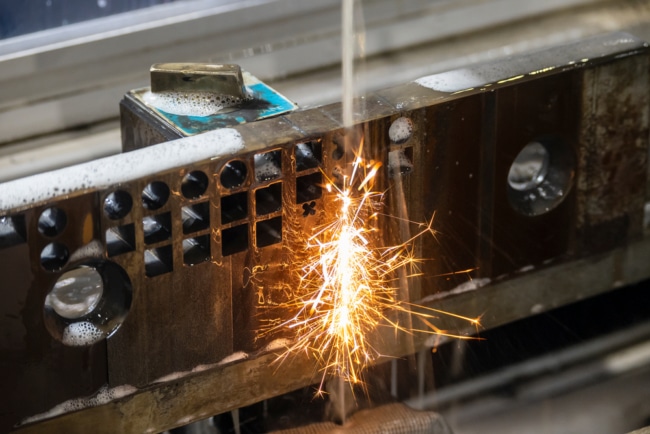
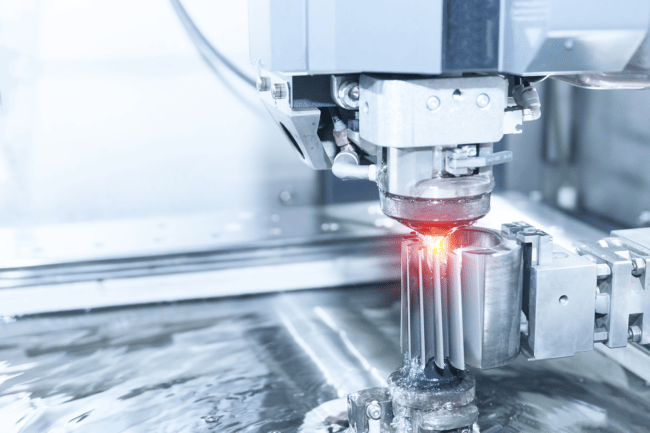
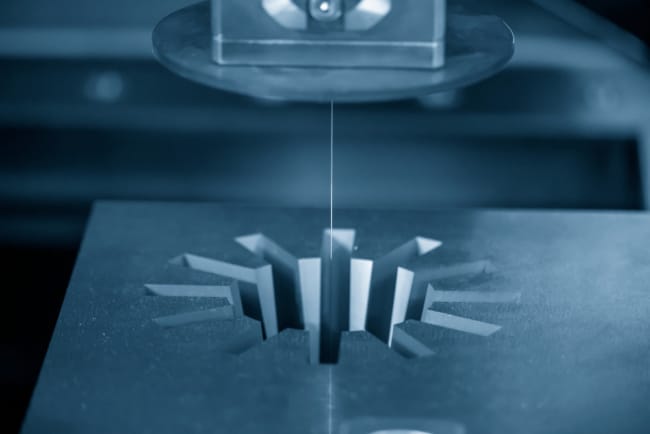
CNC machining is a precise way to manufacture parts. There are two main types of CNC control; milling and turning. And there are differences between the two, despite their very similar operations. For instance, CNC turning holds the cutting tools while the materials rotate around. On the other hand, milling rotates the cutting tools as the materials are held in place. Each one has its advantages, so here is a quick overview of the CNC milling and turning processes.
A Basic Overview of CNC Milling
CNC milling is when the materials are held in place rather than the cutting tool. Because of this, milling requires the use of multiple axes using a cartesian coordinate system along X, Y, and Z. However, a CNC mill requires more configuration time than standard turning lathe machines.
The uses of CNC milling are vast. But like any process, there are disadvantages and advantages. Some of the most useful advantages of milling are being able to manufacture products from a wide range of common materials in a very fast, precise and efficient manner.
Basics of CNC Turning
CNC turning is similar to CNC milling. However, the main difference is that the cutting tools are stationary while the materials rotate. Turning machines can operate along three axes, just like mills. Though there are some specialist machines that can use up to six axes for a project.
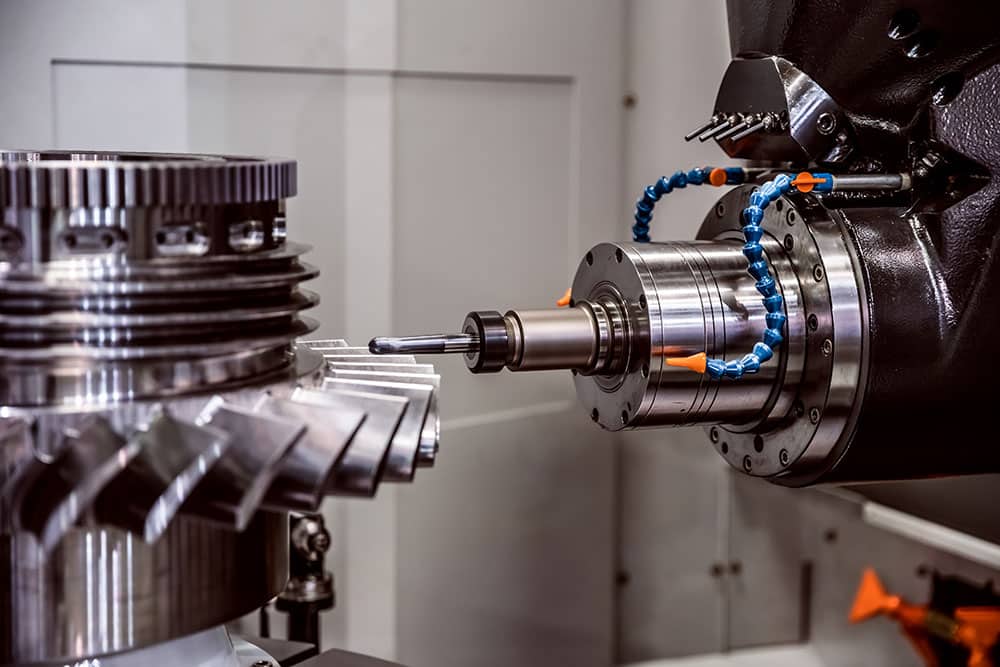
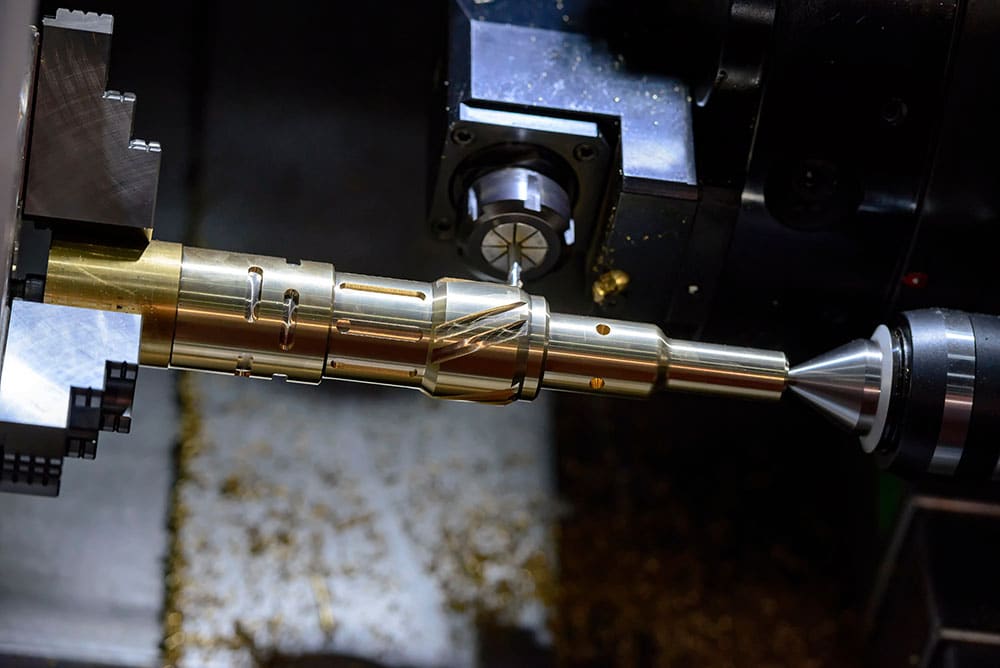
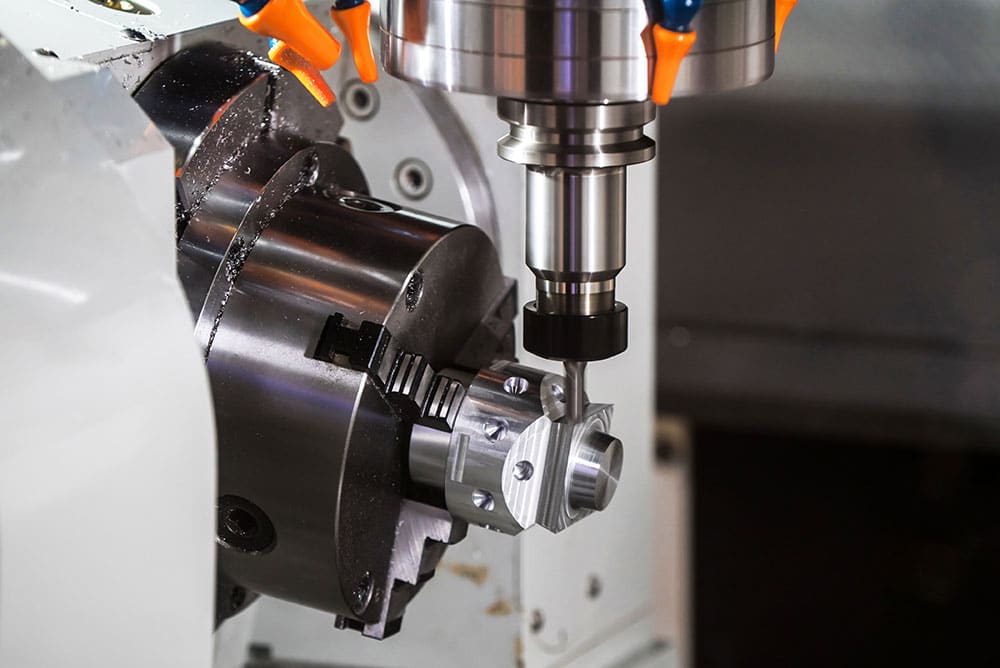



Main Differences Between CNC Milling and Turning
Both CNC milling and CNC turning are similar in operation. But there are distinct differences and characteristics. For instance, with CNC turning, the material rotates and has bits subtracted to create a shape by a moving cutting tool. For milling, a rotating cutting tool works on the material.
Key Considerations
There is no industry untouched by CNC machining. From technological medical advancements such as bionic limb manufacture to intricate components for aerospace designs, any reputable CNC precision engineering company such as A&M can help with your next CNC project.
The ease-of-use and relative cost-effectiveness of CNC for large-scale manufacture makes it a suitable method for almost any business. Because of this, there are many applications to produce products such as custom jewellery, replacement car parts and wooden accessories.
Due to the rapid production volume with a high degree of accuracy, some industries work hand in hand with CNC companies. For instance, aerospace parts must be extremely precise for safety across many material types. And CNC is the only method to offer the required flexibility.
CNC Milling Machines
There are many types of CNC milling machines. Some of the most common include horizontal and vertical, bed mills and popular C-frames. All have distinct uses and advantages for different project types. For example, C-frame mills are popular because they use less shop floor space.
CNC Turning Machines
Generally speaking, there are two types of CNC turning machines; horizontal and vertical. However, there are sub-categories within these defined by their overall scope and axis abilities. There are many available types. But here are some of the most common CNC machine types:
CNC routers that use motors and drivers to cut less accurate products.
Pick and place CNC devices that can work on intricate electronic components.
3D printers are a type of CNC machine and are more reliant on CAD and CAM.
Lathe machines are common and produce products from a single-point rotation.
Plasma and laser cutter CNC machines are extremely powerful and accurate.
These are only a handful of the available CNC machine types. There are, of course, CNC mills, grinders and drills. 6-axis machines and electrical discharge CNCs are less common.
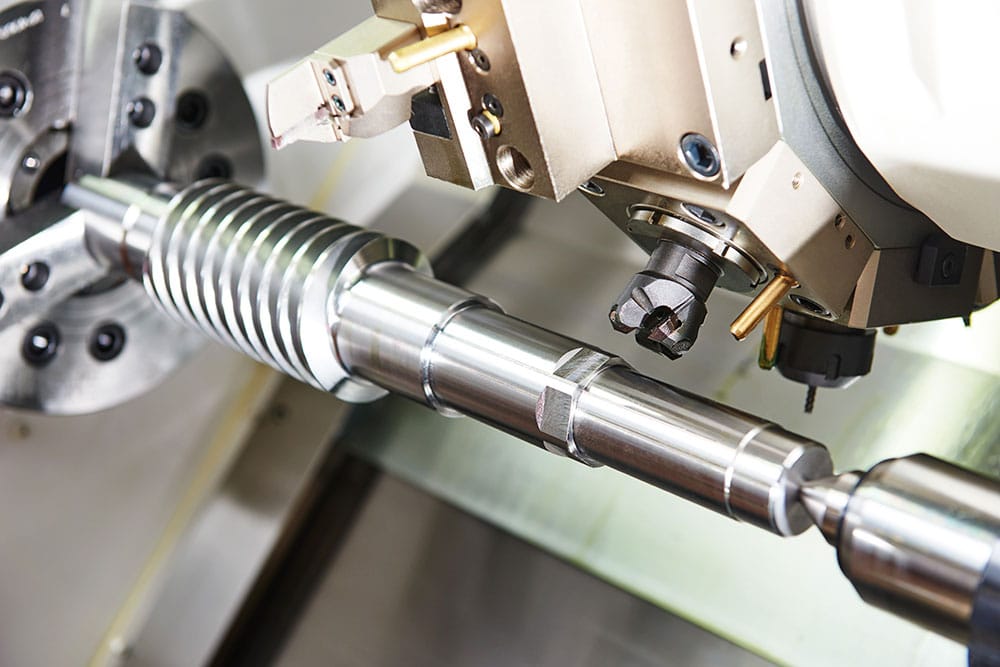
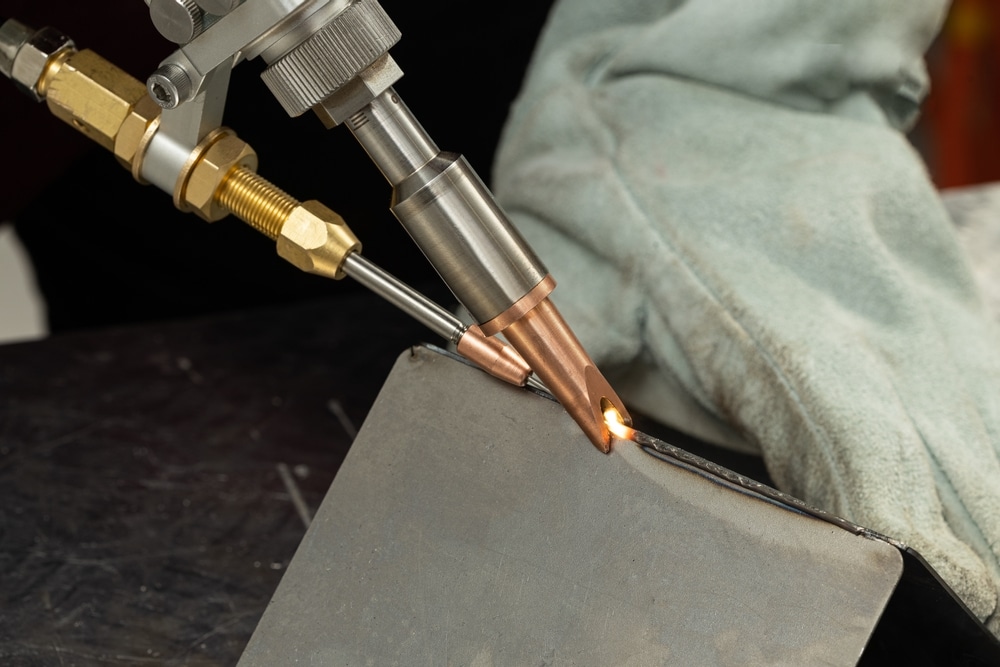


Applications of CNC Milling and Turning
The applications of CNC machining are wide-reaching. Yet there isn’t a blanket approach to a project since each one is unique. Therefore you must consider certain factors of each CNC method, such as operations that need to be performed. But also speed, load and tool life.
Further, the machine, method and programs you choose will determine what materials you can use for your project. Not all materials are suitable for CNC, but some of the most common are:
Metallic substances such as steel, aluminium and copper or brass.
Modern plastics like acetal, acrylic materials and polycarbonates.
Lightweight and durable carving and rigid foam cut for home insulation projects.
Wooden components from hardwoods like oak to manufacturing wood such as MDF.
Exotic metals for specialist applications like titanium, nickel and super duplex alloys.
You also need to consider the speed and accuracy of your project. For large-scale manufacture, you will need industrial-grade mills[7] like Haas CNC machines for 24-hour continuous operation.
The complexity of your project design also comes into play, and not all machines are capable of extremely intricate cutting. Desktop and benchtop CNC machines are great for hobby projects and small businesses. But larger machines offer better rigidity, motor speed and precision.
Conclusion
There is a difference between CNC milling and CNC turning, despite their very similar styles. CNC milling holds materials in place and rotates cutting tools. On the other hand, CNC turning rotates the materials and uses stationary cutting tools. Because of this, each is suited to different projects. For instance, CNC milling is good for plains and faces, while CNC turning is better for more intricate 3D production. Yet each works well with metals, woods and plastics.
Related Content
Need more information?
To see how A&M could support your next complex manufacturing project – simply call us, or use the form below.