In order to understand the difference between Sinker and Wire EDM it is first necessary to have a solid understanding of Electrical Discharge Machining. Therefore we will provide a quick overview of EDM before looking at the particular intricacies of Sinker EDM and Wire EDM. These two are often confused so we will look at what is involved with each process and identify the applications that each is best suited to.
Electrical Discharge Machining Overview
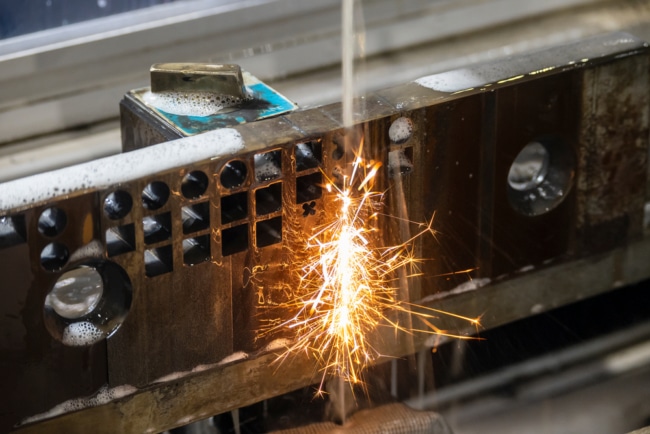
Electrical Discharge Machining can be simply explained as a metal fabrication process, where a specific shape is achieved through the use of electrical discharges.
EDM is an effective non-traditional machining process, and it works by releasing a series of electrical discharges between electrodes, in deionised fluid, to remove material and create a specific shape. It’s a very popular method thanks to its workability, as you can shape a wide variety of different materials of all strengths.
EDM offers consistent results and is particularly well-suited for parts that require tight tolerances. As a result, extra fine surface finishes can be achieved, along with near-perfect perpendicularity.

Sinker EDM vs Wire EDM Explored
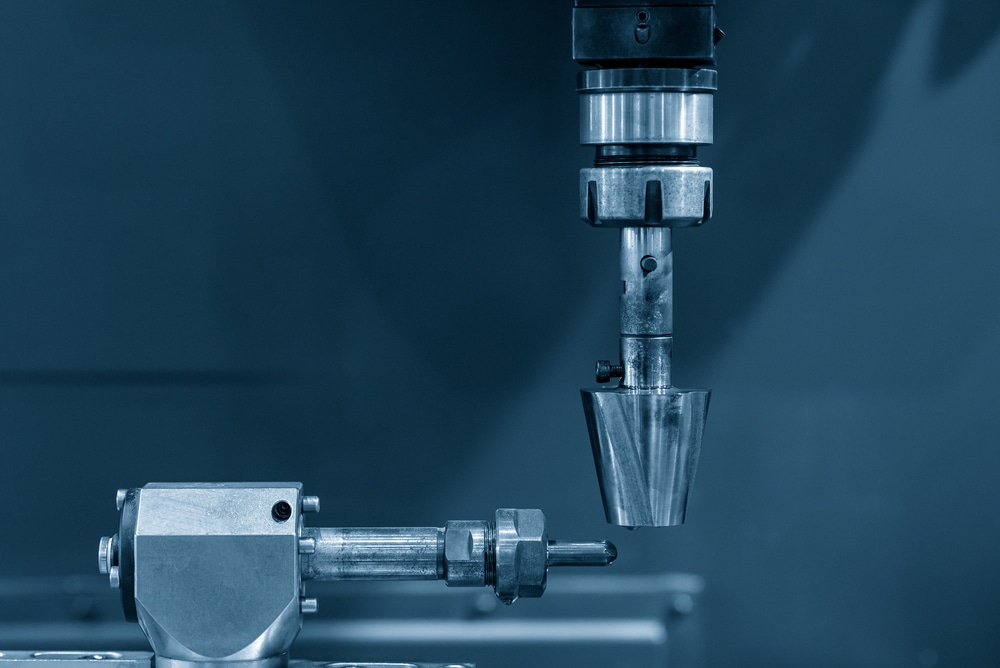
Sinker EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) and Wire EDM are two popular machining techniques used in various industries. Both methods utilize electrical currents to remove material from a workpiece and create complex shapes, but they differ in their approach and application.
What is Sinker EDM?
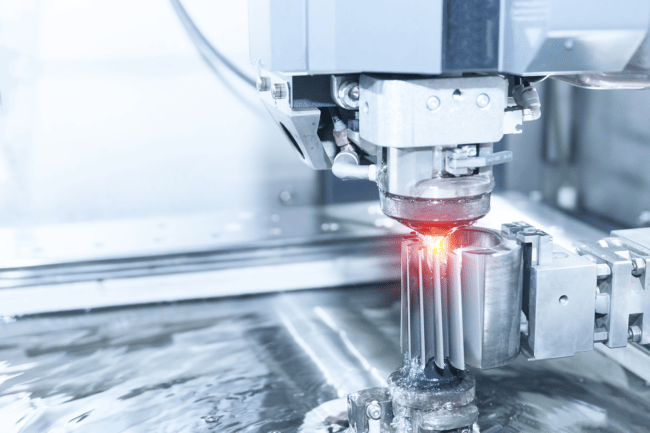
Sinker EDM is commonly referred to by a variety of different names, including RAM EDM, Cavity EDM, Volume EDM and Conventional EDM. During the sinker EDM process, the charged electrode burns into the surface of the material in order to create a specific shape.
The material itself is immersed in oil which stops any debris from sticking to the surface, and the electrodes are generally made out of varying materials which will be specifically matched to certain metals and alloys that are present inside the material.
When the process has been completed and all excess parts removed, the base metal will have been clearly eroded presenting a specific design like an engraving. The most common materials include copper, brass and graphite. Dissimilarly from wire EDM, sinker EDM doesn’t actually cut all the way through the material - instead, it cuts the surface at a depth that can be set to any required number.
What is Wire EDM?
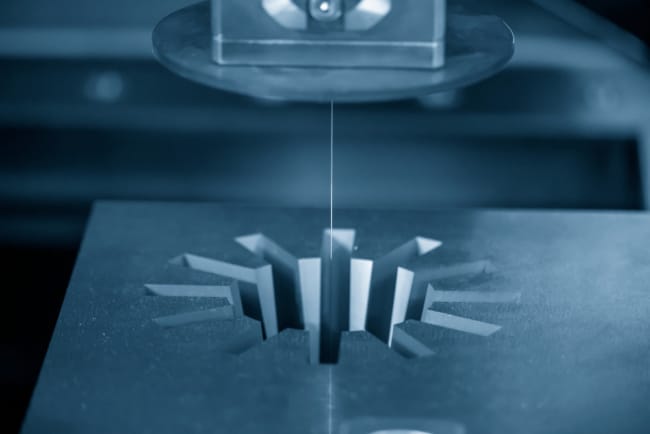
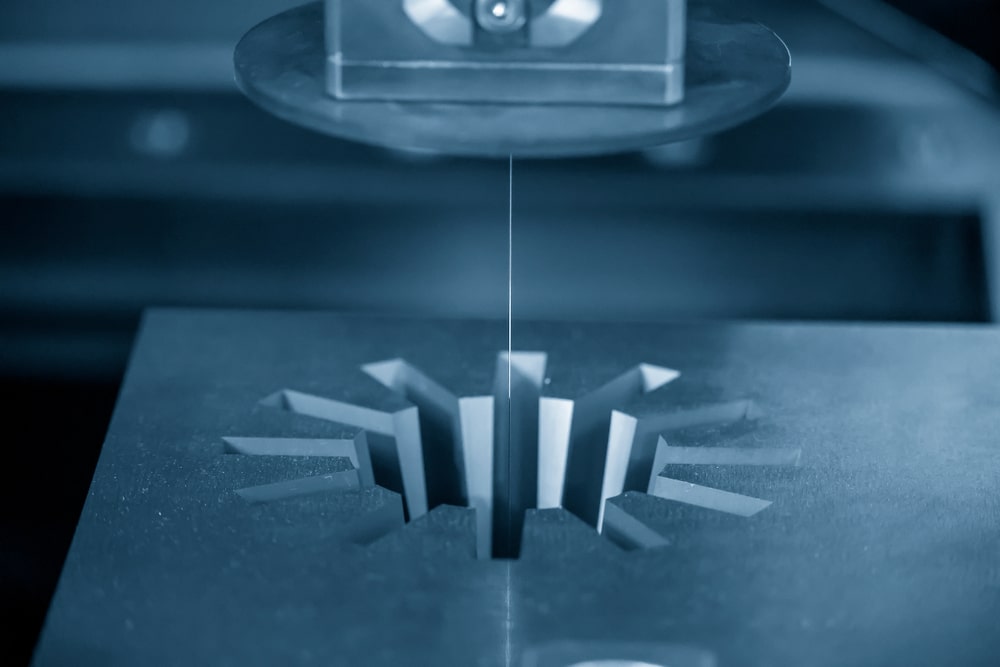
Wire EDM machines work in a similar way to sinker EDM devices as described above, but they use a rapidly charged, conductive metal wire to melt through the material. No contact is made between the wire and the material itself, as this will remove the risk of any distortion of the wires path, while also limiting the likelihood of damage too. Sparks basically jump between the wire and the material, and this is how excess material is removed. A wire EDM machine can be used in a variety of different working environments, for a number of applications.
Sinker EDM Applications and Features
Sinker EDM can be utilised on any material that is electrically conductive. It allows for complex shapes to be created, even in the hardest materials used in manufacturing. Sinker EDM is a good choice for the most precise manufacturing processes, as it can work well even when there are sharp corners that call for a tight radius.
Wire EDM Applications and Features
Wire EDM is capable of cutting through relatively hard materials, and it is fair to say that is nearly always utilised when you need to cut all the way through a material rather than marking the surface. This is the biggest difference between wire and sinker EDM, as sinker is generally used to make nothing more than cavities whereas wire can cut from one face to another. During the wire EDM process, wire itself is usually made out of a brass material. This process is typically used to cut right the way through very thick pieces of strong metal, and it typically produces a great surface finish.
Applications of Sinker EDM
There are many sinker EDM applications, including but not limited to:
Rapid Tooling
Mold making
Injection molding molds
Dies
Fine details
Sharp inside corners
Deep and thin ribs
Blind cavities
Blind keyways
Internal splines
Threads
Applications of Wire EDM
There are a number of wire EDM applications, such as:
Thick plates
Extrusion dies
Blanking punches
Automotive and aerospace parts
Tight-tolerance parts
Medical and dental devices
Parts where burrs are unacceptable
Thin parts that could break during conventional machining
Graphite electrodes for sinker EDM
Conclusion
Understanding the pros and cons of both sinker EDM and wire EDM can be extremely beneficial for businesses looking to access the most suitable technology that can match up with their unique needs. It’s clear to see that the main difference between sinker EDM and wire EDM is the depth at which the process is able to cut, as sinker EDM generally leave a kind of cavity or engraving, whereas wire EDM can slice cleanly all the way through. Both EDM types are extremely reliable and accurate, and you can expect to achieve brilliant results when you can access the right kind of EDM process for your individual requirements.
In short, both sinker EDM and wire EDM have a range of applications and selling points which make each one just as essential in different settings and situations.
Related Content
Need more information?
To see how A&M could support your next complex manufacturing project – simply call us, or use the form below.